Bytelocker in C
I loved locking up folders as a kid on the Windows 7 computers using batch scripts I didn't understand.
# Welcome to the bytelocker!
This is a small program written in C to help me consolidate by understanding of `FILE` streams, *bitwise operations* and *memory representations* of data.
## What does bytelocker do?
Bytelocker takes in 2 arguments, a file and a password. It then encrypts this file in place with an ECB cipher.
## Why is this useful?
Whilst you can use this binary from the command line to encrypt a standalone file, as is the case with many `C` programs, you will find this integrates nicely within larger workflows. See below.
### My usecase.
I spend my day in vim and vimwiki. And sometimes I need to document slightly sensitive information which I don't feel comfortable leaving in plaintext. As such, I have added a binding to my vimrc calling the bytelocker utility.
The code snippet looks like:
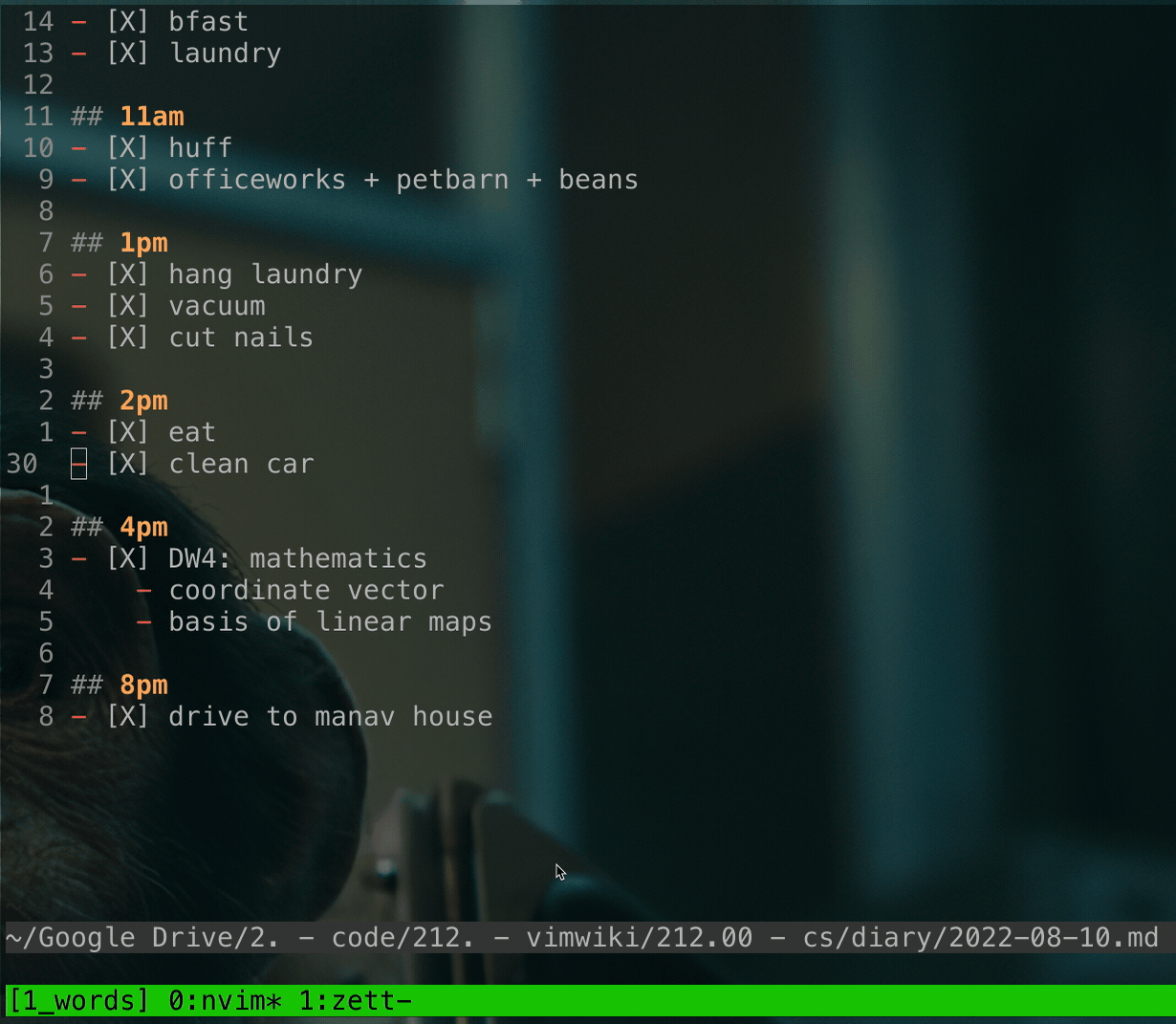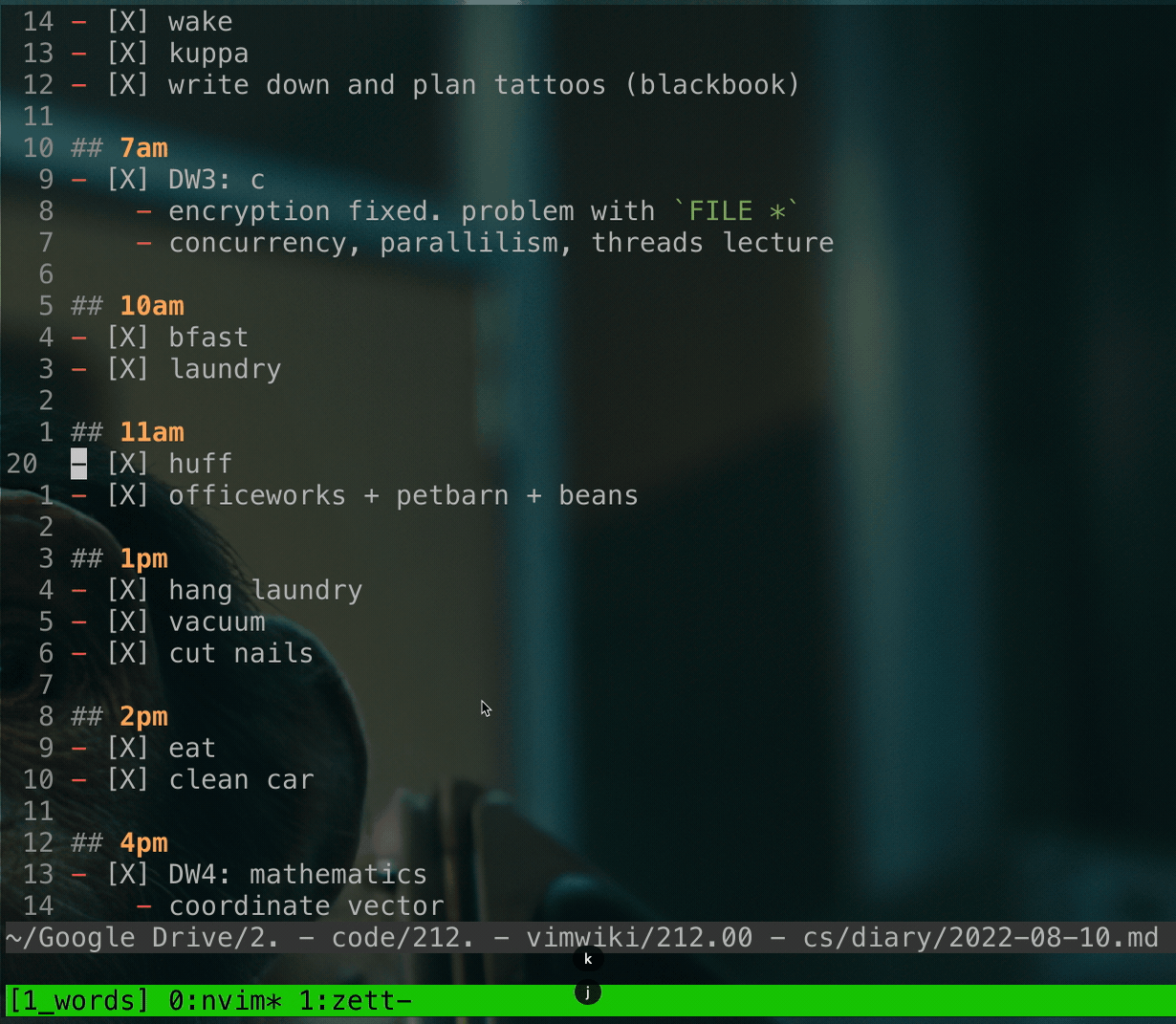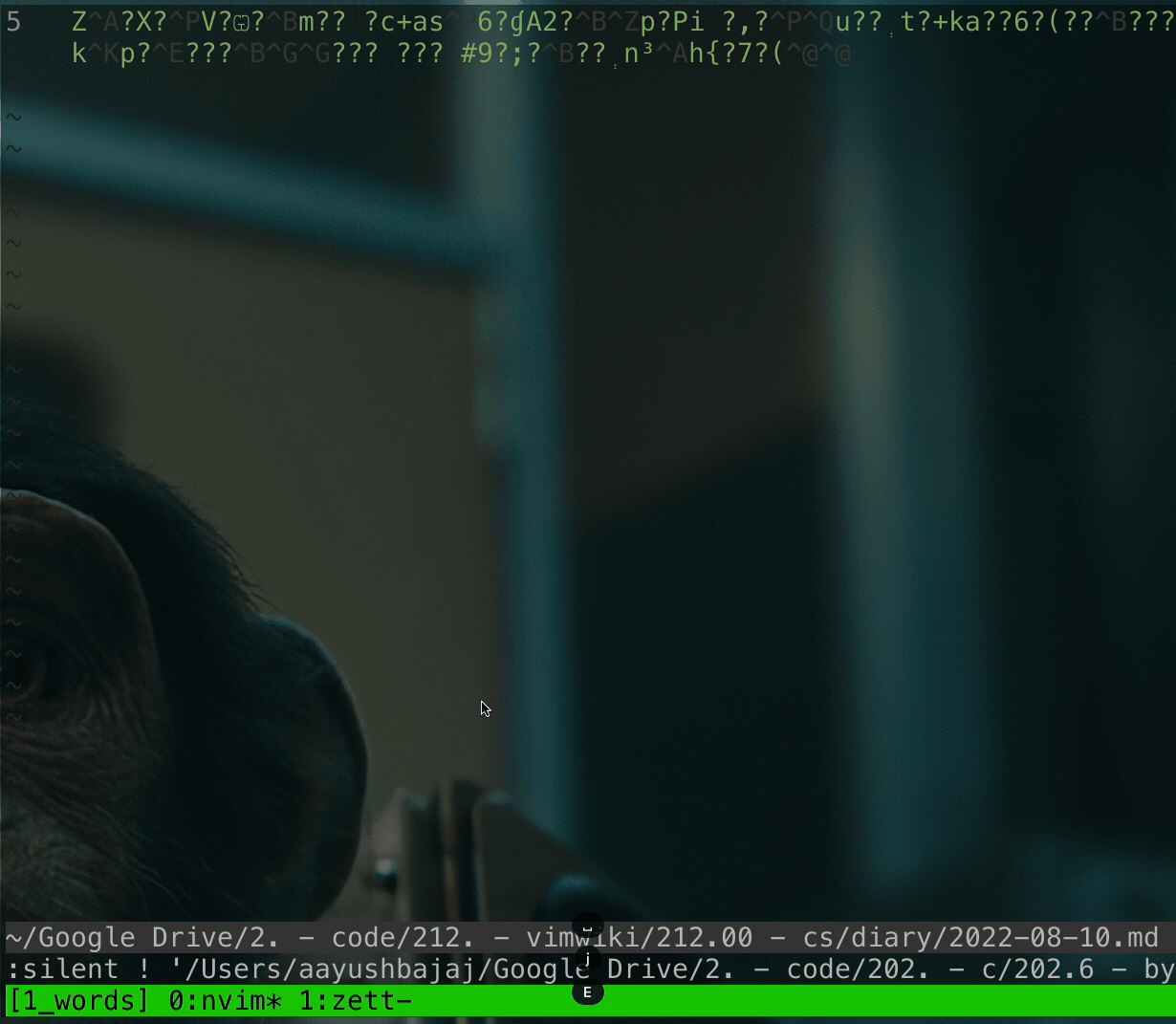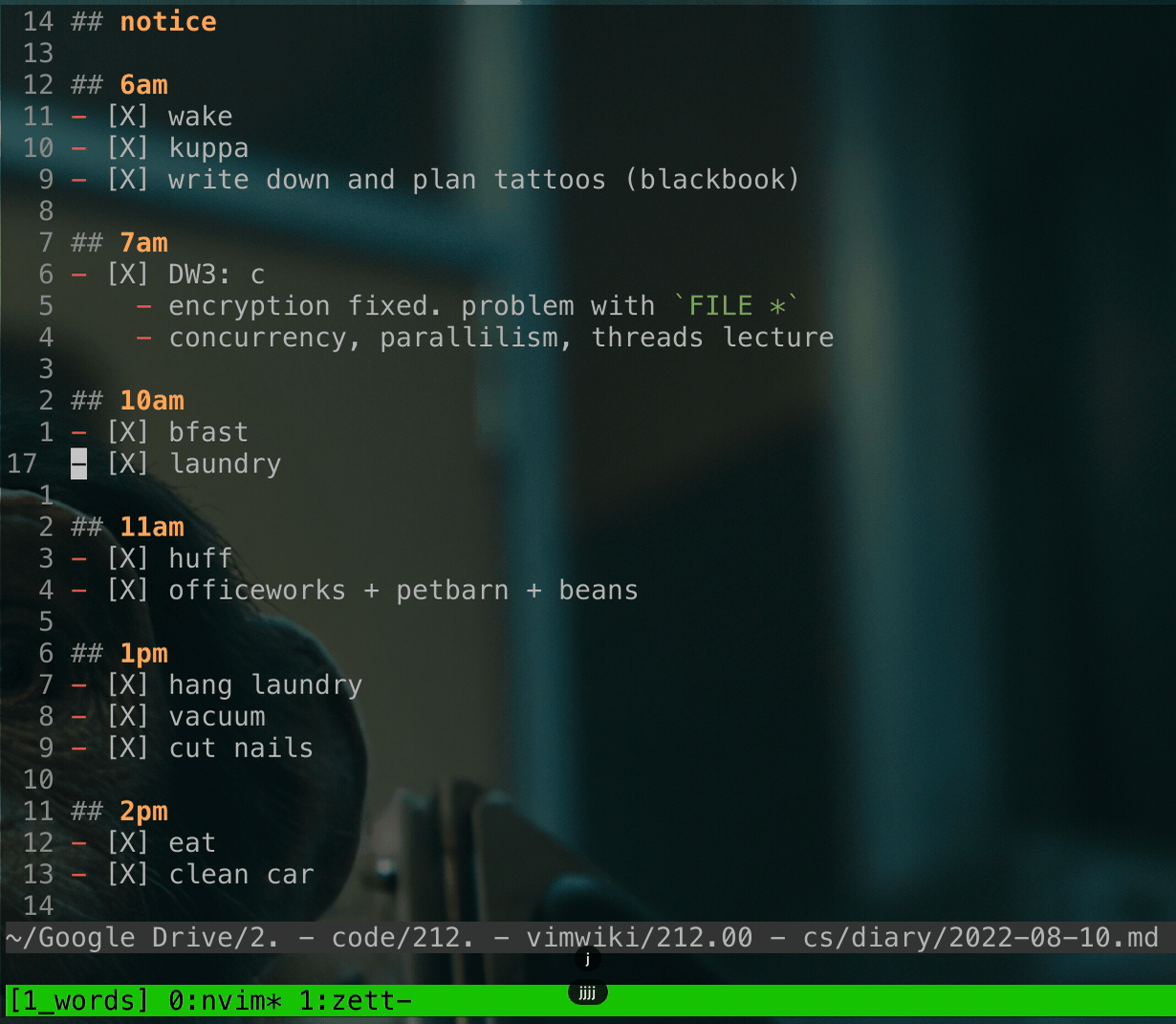
`nnoremap E :silent ! '/Users/aayushbajaj/Google Drive/2. - code/202. - c/202.6 - bytelocker/bytelocker' '%' '$bl_pass'<CR>:set noro<CR>`
here pressing capital E in normal mode will encrypt the file.
- `silent` suppresses output
- `!` is the execution of a shell command, which then runs the bytelocker executable from my google drive
- `%` is a vim macro for the current file
- and the password is retrieved from an environmental variable defined in `.zprofile`.
- the definition looks like `export bl_pass="passwordpassword"`
- **NOTE: the password must be 16 characters!!**
- **NOTE: if you choose to define the password in another file, make sure your viwrc sources the file**
- the line in .vimrc would look something like `so "~/.config/zsh/.zprofile"
### Demo
tl;dr this used to be a standalone repo.
demo
code
makefile
CC = clang
CFLAGS = -Wall
.PHONY: all
all: bytelocker
bytelocker: bytelocker.c bytelocker.h main.c
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) main.c bytelocker.c -o bytelocker
.PHONY: clean
clean:
-rm -f bytelocker
bytelocker.h
#ifndef _BYTELOCKER_H
#define _BYTELOCKER_H
#include <stdbool.h>
#define MAX_PATH_LEN 4096
#define MAX_LINE_LEN 2048
#define RAND_STR_LEN 16
#define CIPHER_BLOCK_SIZE 16
bool test_perms(char filename[MAX_PATH_LEN]);
void encrypt_f(char *f, char *pass);
void decrypt_f(char *f, char *pass);
char *shift_encrypt(char *plaintext, char *password);
char *shift_decrypt(char *ciphertext, char *password);
char *rand_str(int seed);
#endif // _BYTELOCKER_H
bytelocker.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include "bytelocker.h"
const char *const MSG_ERROR_FILE_STAT = "Could not stat file\n";
const char *const MSG_ERROR_DIRECTORY =
"bytelocker does not support encrypting directories.\n";
const char *const MSG_ERROR_READ =
"user does not have permission to read this file.\n";
const char *const MSG_ERROR_WRITE =
"user does not have permission to write here.\n";
void encrypt_f(char *f, char *pass) {
char line[16];
int r;
FILE *f_r = fopen(f, "rb");
FILE *tmp_w = fopen("tmp.txt", "wb");
// writing a null character at start of file to indicate encrypted
fwrite("\x00", 1, 1, tmp_w);
// writing encrypted characters to tmp
while ((r = fread(line, 1, sizeof line, f_r)) != 0) {
if (r != 16) {
for (int i = r; i < 16; i++) {
line[i] = '\x00';
}
}
fwrite(shift_encrypt(line, pass), 1, 16, tmp_w);
}
fclose(tmp_w);
fclose(f_r);
// writing encrypted characters to original file
FILE *f_w = fopen(f, "wb");
FILE *tmp_r = fopen("tmp.txt", "rb");
int c;
while ((c = fgetc(tmp_r)) != EOF) fputc(c, f_w);
fclose(f_w);
fclose(tmp_r);
remove("tmp.txt");
}
void decrypt_f(char *f, char *pass) {
char line[16];
int r;
FILE *f_r = fopen(f, "rb");
FILE *tmp_w = fopen("tmp.txt", "wb");
// gobbling first null character
fseek(f_r, 1, SEEK_SET);
// writing decrypted characters to tmp
while ((r = fread(line, 1, sizeof line, f_r)) != 0) {
if (r != 16) {
for (int i = r; i < 16; i++) {
line[i] = '\x00';
}
}
fwrite(shift_decrypt(line, pass), 1, 16, tmp_w);
}
fclose(tmp_w);
fclose(f_r);
// writing decrypted characters to original file
FILE *f_w = fopen(f, "wb");
FILE *tmp_r = fopen("tmp.txt", "rb");
int c;
while ((c = fgetc(tmp_r)) != EOF && c != '\x00') fputc(c, f_w);
fclose(f_w);
fclose(tmp_r);
}
bool test_perms(char filename[MAX_PATH_LEN]) {
// 4 cases:
// - checks if file exists
// - must be a regular file
// - user must be able to read file
// - user must have premissions to write
struct stat s;
// checking if a file exists
if (stat(filename, &s) != 0) {
printf(MSG_ERROR_FILE_STAT);
return false;
}
// checking if file is a folder
else if (s.st_mode & S_IFDIR) {
printf(MSG_ERROR_DIRECTORY);
return false;
}
// checking if user can read file
else if (!(s.st_mode & S_IRUSR)) {
printf(MSG_ERROR_READ);
return false;
}
else if (!(s.st_mode & S_IWUSR)) {
printf(MSG_ERROR_WRITE);
return false;
}
else return true;
}
char *shift_encrypt(char *plaintext, char *password) {
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
uint8_t k = plaintext[i];
for (int j = password[i]; j > 0; j--) {
k = k << 1 | k >> (8 - 1);
}
plaintext[i] = k;
}
return plaintext;
}
char *shift_decrypt(char *ciphertext, char *password) {
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
uint8_t k = ciphertext[i];
for (int j = password[i]; j > 0; j--) {
k = k >> 1 | k << (8 - 1);
}
ciphertext[i] = k;
}
return ciphertext;
}
// and must be freed by the caller.
// generates random string of length 16
// same seed returns same string
// string composed of upper, lower and 0 - 9
char *rand_str(int seed) {
if (seed != 0) {
srand(seed);
}
char *alpha_num_str =
"abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"
"ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"
"0123456789";
char *random_str = malloc(RAND_STR_LEN);
for (int i = 0; i < RAND_STR_LEN; i++) {
random_str[i] = alpha_num_str[rand() % (strlen(alpha_num_str) - 1)];
}
return random_str;
}main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "bytelocker.h"
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
// argv[1] = filename
// argv[2] = password
if (argc != 3) {
fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s <file to encrypt / decrypt> <password>\n", argv[0]);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
if (!test_perms(argv[1])) {
fprintf(stderr, "Do not have appropriate permissions on %s\n", argv[1]);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// checking first byte of file to see if it is ascii
FILE *f = fopen(argv[1], "r");
char check[1];
fread(check, 1, sizeof(check), f);
ungetc(check[0], f);
fclose(f);
// encrypts if ascii, otherwise decrypts
if ( check[0] > 31 && check[0] < 127 ) {
encrypt_f(argv[1], argv[2]);
}
else {
decrypt_f(argv[1], argv[2]);
}
}